Back to Lecture Thumbnails

rahulahoop

pranil
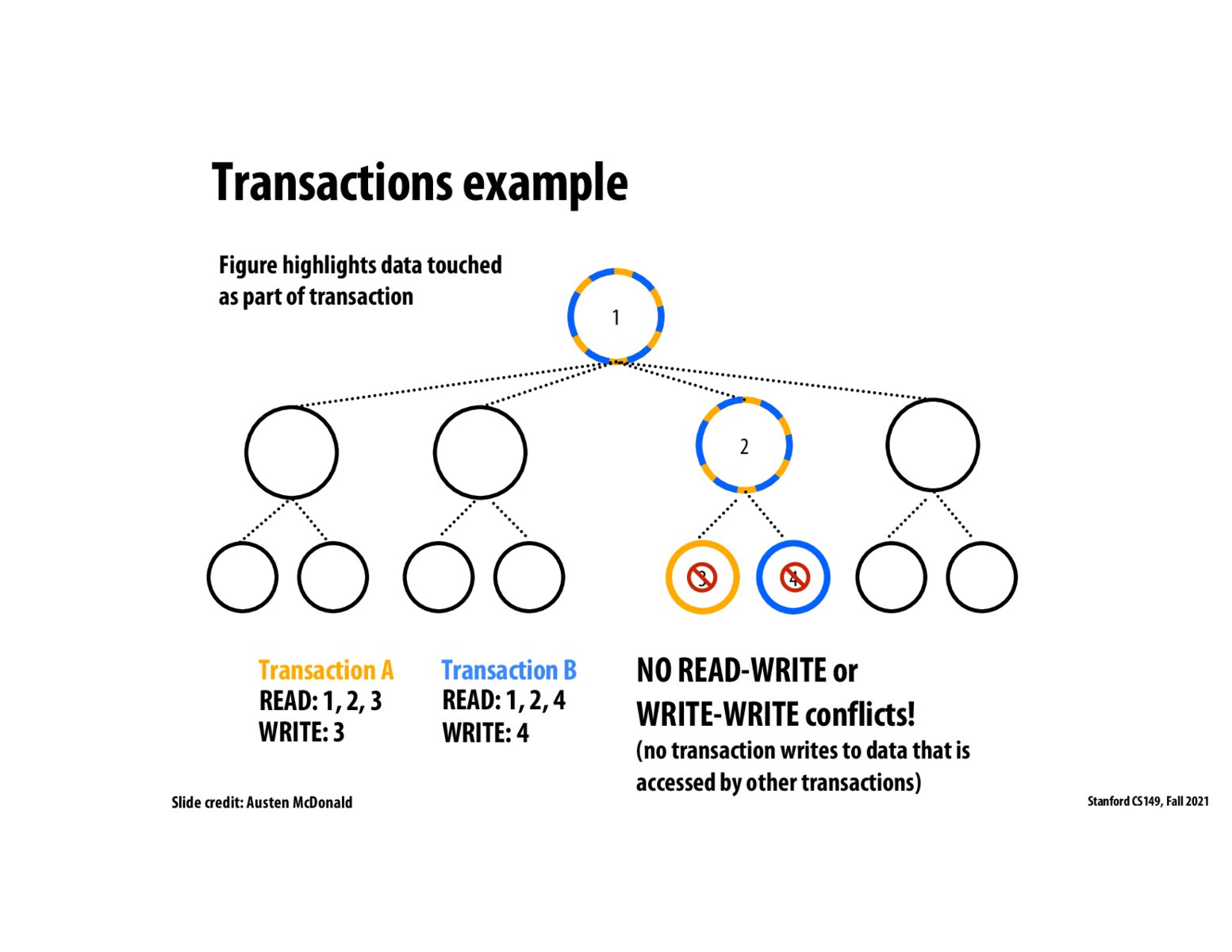
Here's a more elaborate way of thinking about this: The issue is arising because both the paths from the root to both these leaves have a lot of overlap. Even though the tasks ('updating the leaf node') themselves are independent of each other, using locks would cause an unnecessary loss of concurrency. This is where transactional memory does a better job. Each transaction proceeds to update one leaf node in its own atomic region simultaneously. And then, both transactions are able to successfully commit their changes as no conflicts are detected. In this case, there is no synchronization overhead at all.
Please log in to leave a comment.
Copyright 2021 Stanford University
The hand-over-hand locking approach that we used for linked lists would also serve as a correct solution to making trees threadsafe. However, doing so would make them incredibly inefficient. The threads that we see in this slide are not modifying the same leaf in our tree, but because of the synchronization protocol in place, the two threads cannot execute concurrently.