Back to Lecture Thumbnails

tsk

lwzt
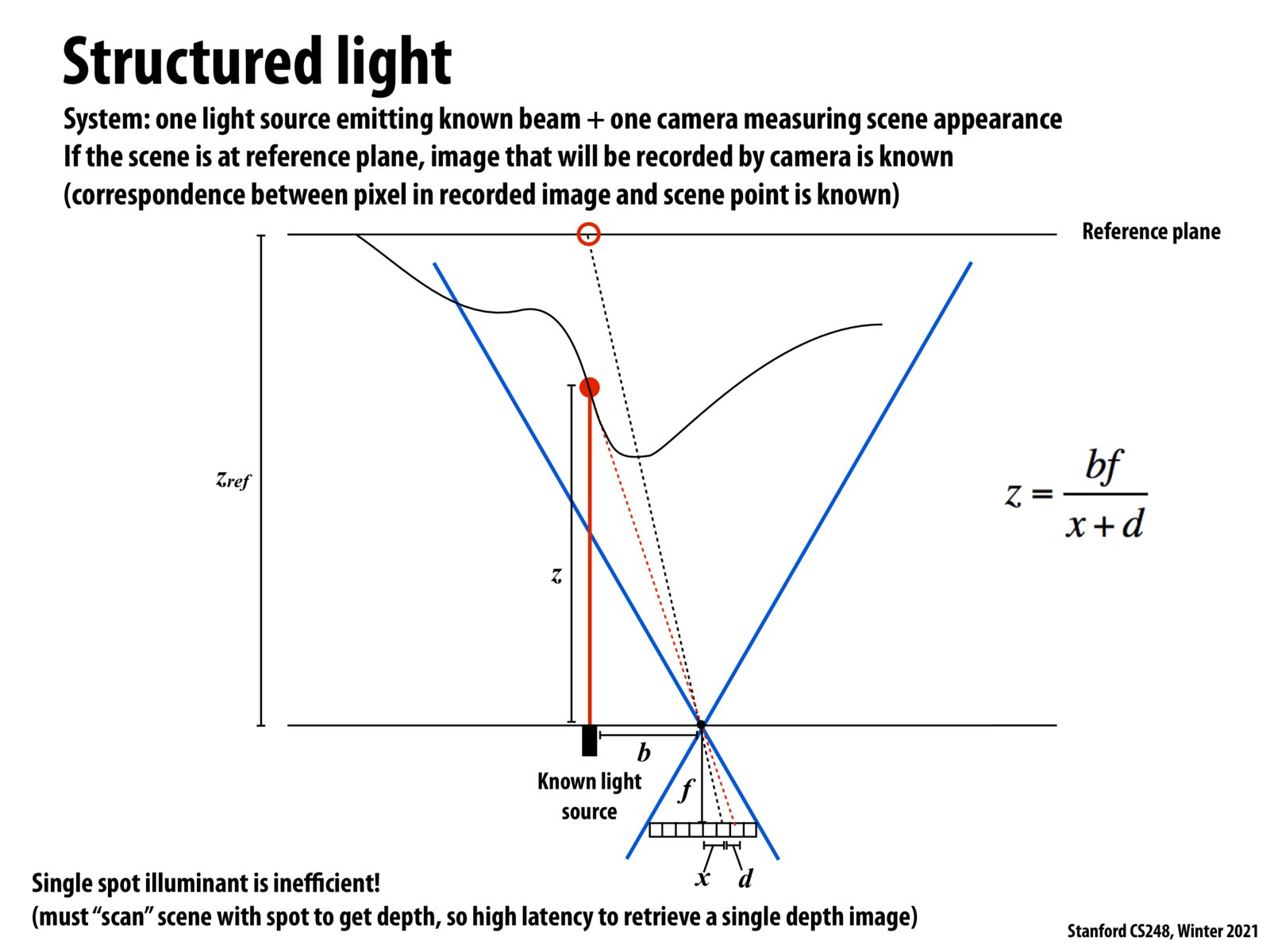
To get the equation on this slide, we aren't eliminating Z_ref. Instead, we are just taking the b / z = (x + d) / f equation and re-arranging it with the following steps:
- bf = z * (x + d)
- z = bf / (x + d)
The equation for x / f = b / Z_ref was the reference for getting the value of x by using like triangles to estimate the result of the reflected light actually reaching the Z_ref point.
Knowing this reference point, we can now compute the actual distance of the point in front of the light source, z.

tsk
Thanks for the clarification!

sman64
It seems like the curve is blocking the red ray from reaching the reference plane so how would we measure z_ref?
Please log in to leave a comment.
Copyright 2021 Stanford University
In the lecture, there are two equations:
x / f = b / Z_ref
b / z = (x + d) / f
How do we eliminate Z_ref and get the equation on this slide?