

Excited to take 348E next quarter.

Jumping on the train - thanks for a fantastic course!

Thank you for the fun course! I learnt so many useful concepts.

Thank you Kayvon! It's really the best class in my life. I hope to have an opportunity to take CS149 and CS348K in the future. Also thanks all the TA for your help too!

I think it's various for different technology. For exampel for LED screen, it uses backlight at lot so a brighter screen may impact battery life a lot. But for e-ink display, it's a different story. However I'm not sure if the grayscale on e-ink display can be treated as brightness though.

do rod cells also have LMS response functions?

Thanks to Kayvon and the TA's for all their hard work to make a virtual class interactive and fun!

There are only two generations of RTX cards that support hardware ray tracing, so companies probably need more time to integrate ray tracing into their games. But I have seen many newer titles with ray tracing support.

Thank you! Learned a lot from the course.

Thanks for the great course!

What's the difference between sharpen and contrast? can we use a filter to change contrast?

what's the purpose of this layer of metal?

thank you so much!!! i really loved taking this class

what kinds pf properties does the leftmost object feature? that looks fantastic! (subsurface scattering, translucence, etc?)

does this only apply to fully opaque triangles? or how are alpha values taken into account here

Best class I've taken at Stanford so far! Thank you!

I'm still a little confused about this method. If we sort the geometry first, don't we still need to perform pixel-level depth tests at the Frame-Buffer Ops step in case of geometry intersection? If this is the case, where does the optimization come in?

When viewing a 360 video in VR, there often is some distortion and what you are viewing. Is there a way to cut back on this distortion?

The retina has layers of neurons, some of which that are uniformally spread and pool from many photoreceptors, some of which are shared with other neurons. This could be thought of as being analagous to convolutions!

It is very easy comparatively to tell what should be in focus if a user taps the area of the image they want in focus!

I'd be interested in seeing a visualization of "tone mapping" in humans as people adapt to different lighting environments.

The contours of the woman's face are also too angular due to an insufficent amount of polys. The skin also looks weird because its material is too smooth and diffuse.

Even though recent RTX cards have real-time ray tracing, I have not really seen a lot of adoption of it in applications such as games, probably due to its currently low market share. When do you think ray tracing will have widespread adoption by the larger market?

How do these cameras account for motion in the surrounding?

Best class ever!

I think most GPUs have almost there own programming language(I know Nvidia has cuda) so you can manage how individual tasks are done on the GPU and by which unit.

Is this in the context of motion only? So in that case there are t copies of the pixels and vector would be more efficient.

A narrower problem is hand pose estimation, with important applications in arthritis detection. Inference on mobile and edge devices is challenging for deep architectures, but there have been rapid advancements including https://ai.googleblog.com/2021/03/accelerating-neural-networks-on-mobile.html

Perhaps topics like representation/reconstruction?

^^^ This has been one of my favorite classes thus far! Thank you!

Thanks Kayvon and TA's for a great quarter!

GPU uses a pointer that points to the visible triangle at a pixel, saving work to check on other triangles in the region.

Though shading only the two-by-two region, only apply colors to super sample points actually in the triangle

Reason to sort: prefer front to back because otherwise early z out doesn't really happen

Not very well versed on computer architecture. But what decides which compartment in the GPU solves which part of the rasterization pipeline?

So this is C1 but not C2 continuous, correct?

I asked in class why only recently has GPU technology for real-time ray tracing emerged. There's a number of factors for why we got within striking distance of real-time ray tracing, including both having enough raw compute power (Moore's law) and improvements in ray tracing algorithms.

Why is the filter always flipped with respect to the image? I've never understood why we flip the filter before convolving (obviously it makes no difference for simple blurs, but for other operations it's impactful).

My understanding was that color blindness occurs as a result of a shift in the medium and long wave length response functions in the associated cones towards each other, resulting in red and green being specifically harder to differentiate.

Newton's method is also good option to find minimums but can be computationally costly due to the calculation of Hessian

From this equation, we can also see that part of the reason why we can use simple RGB-driven displays/devices to match with human eye perception is because we only have three types of cone cells/spectral response functions.

RGB are the primary colors of light, and CMY are the primary colors of pigment.

Found a great video explaining the concept of CoC https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Pdq65lEYFOM

Not really a comment, but take CS149! It covers this material in alot more depth!

It is used in PPT when we try to draw an animation path!

There are many second-order optimizers that can speed up the optimization, comparing to the first-order methods like gradient decent, one is ADAM which is often used in DNN.

GPUs are optimized for throughput while CPUs are optimized for latency.

This really highlights the way assignment 3 brings the rendering pipeline all together!

The new iPhone 12 has LiDAR, which is a more direct way of capturing 3D information. Solid state LiDAR systems are also coming to market.

My guess is that the brighter the screen, the shorter the battery life because it uses more power. But I think there are more factors influence it.

What's the relationship between screen brightness and battery life?

@mrn someone else shared this earlier and I thought it was really helpful: https://setosa.io/ev/image-kernels/

I think this motion capture use case at Boeing is really neat: https://www.boeing.com/company/key-orgs/boeing-technology-services/additional-services.page
Using motion capture to estimate joint stress and fatigue when performing a task.

But we could define a spline in a way that requires it to pass exactly through the points, correct?

Why does the graphics pipeline specify that the depth test is performed after fragment processing, if that results in a lot of wasted work? When is it better to use the process on the left?
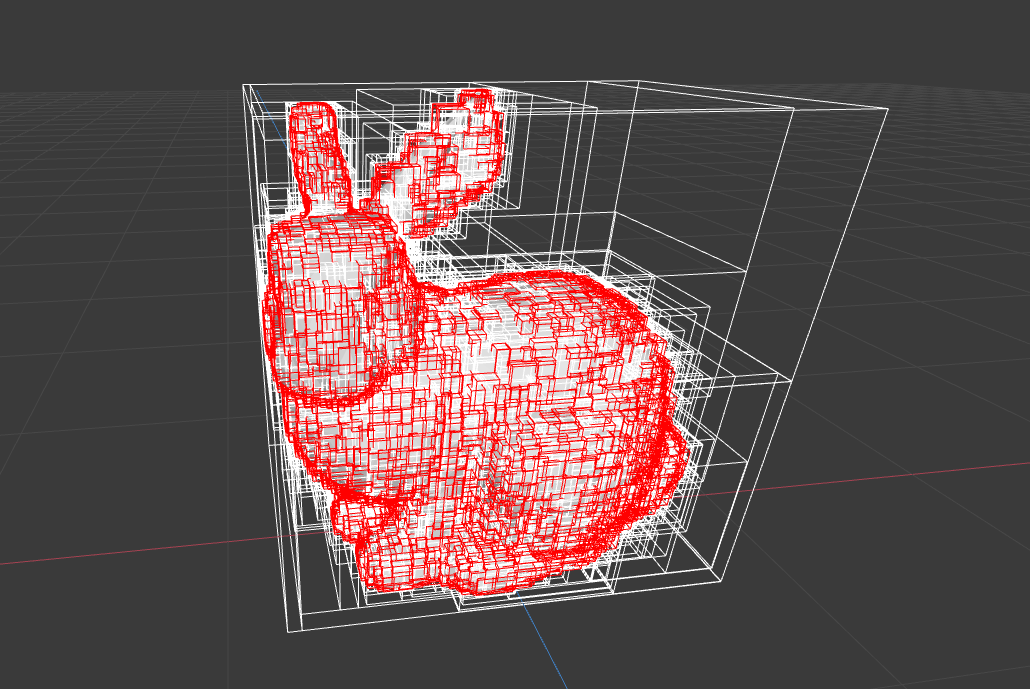
Is the trade off here between memory read and write? I think there could be a memory read for verifying that tiles' content is the same as the last frame.

Apple animoji uses Apple's TrueDepth Camera, not the infrared camera as publicized.

Are there any significant architecture difference between mobile and larger GPUs?

How do we define control point p1/p2 here?

BM3D is one of sota classical denoising algorithm, people are also using Neural Network to do denoising https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Block-matching_and_3D_filtering

There are a bunch of other optimization algorithms depending on what you want. The gradient descent is the first order derivative but you can also take partial derivatives or second order derivatives.

Infrared light is indeed just light at a different frequency. However, since it's not visible, it could be used to easily generate depth maps of the environment and capture motions without the interference of other visible lights.

How do we convert RGB to HSV?

I guess we have to bound the summed transform someway so the vertex does not behave drastically?

Would you just store coefficients for each of the converted Y, Cb, Cr channels?

So are people who are color blind unable to perceive one of these color axes?

Is there any one 3D capture technology that kind of "took over", or could the structured light approach from the original Kinect still be useful?

Is the benefit of the IR sensor that you're also generating IR light with a laser? So it's more controllable than just pulling in RGB channel information.

Are there other problems in graphics apart from inverse kinematics that are often solved by posting an optimization problem?
@gtier most likely uses VRAM sharing video memory with the rest of the graphics stack. They're usually executed using specialized tensor cores separate from rendering CUDA cores and the like.

Are these models stored with the GPU in VRAM or in firmware?

Is it enough to scan a material scan or do data scientists have to try to fit functions to a materials appearance?

What other descent or traversal methods exist besides gradient descent?

Since we are just setting step size to be small without step control, does this mean we may need a lot of iterations? Otherwise we may not reach the minimum.

@lwzt this is probably just done for convenience/cost reasons - probably hard to "upsample" by "inverting" the gaussian (and empirically unnecessary)

Most likely these are separate steps - you would perform data capture first and then simulate by inserting the captured rigidbodies into the scene. A real time visualization of this might be cool/practical for people working on set though?

Interesting that so much of the world (ie. basically all jpegs) rely on a heuristically tuned quantaization matrix - wondering if there's a way to define a parametrized version of this

As an extension of this idea taken to the extreme you could forego any detail at all and have a network "hallucinate" textures to render a game/environment - https://news.developer.nvidia.com/nvidia-invents-ai-interactive-graphics/?ncid=so-you-ndrhrhn1-66582. Obviously not the same pipeline here but in spirit kinda similar

If people are wondering, eye tracking on consumer devices is quite feasible and possibly the next step in commercial headsets, and a nice thing about eye tracking in addition to just for rendering is for better avatars - see https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q-gse_hFkJM

There's a lot of recent literature/attempts at compressing using small deep nets which replace handcrafted encoders

Wondering what other light sources approximate an infinitely far away light. I used Blender's sunlight simulation in my CS148 project, it was pretty impressive and had an angle parameter. See https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RgJGm-iT5cY.

Here's a paper on evaluation of chromatic aberration methods:
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/314788222_EVALUATION_OF_CORRECTION_METHODS_OF_CHROMATIC_ABERRATION_IN_DIGITAL_CAMERA_IMAGES
From the abstract, they evaluated two general approaches: "The chromatic aberration correction methods evaluated in the experiment are classified into two kinds. One is the method to correct image coordinates by using camera calibration results of color-separated images. The other is the method based on the assumption that the magnitude of chromatic aberrations can be expressed by a function of a radial distance from the center of an image frame."

Really cool <1 minute example of this: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HjHiC0mt4Ts . Note how the subtle things really do add up to create a feeling of both ultra realistic and unrealistic.

Just looking over some of the heuristics in the video, I think many of these are still used. I recall in cs148 it was discussed, that in some scenarios the compute is now worth the quality.

@kasi It looks like its parameterized by roughness: https://docs.blender.org/manual/en/latest/render/shader_nodes/shader/glossy.html

With multiple cameras, computer vision methods like triangulation can be used to locate the 3D position of each marker, and then reconstruct body/joint positions. Besides occlusions, multiple cameras can also help with canceling out noise in each camera view.

@kckckc I think the exit condition is just hitting a primitive. I don't think the max helps.

I actually use this a lot in my video editing!

seems right to me liangcyn, but, it was explained as something that's done to determine if there was collision between frames. So I think the frames are already the lowest level of discretization that's available. For that reason I don't thin the time of intersection is the desired output but merely a boolean.

I think there is also a concept called early z and late z. In case shader is looking up for a texture where it can modify the original z value (like displacement mapping?), then it could change how the final Z value. What we are looking is early z value. It is possible that in real rendering, late z is also enabled. We just update the Z buffer after shader is run. However, we would lose the benefits of hidden surface removal for correctness..

I guess with GPU, we can mimic the lens system by changing pinhole model to a model where ray shoot to a square randomly. In this way, we can get the depth of field feeling as it is in DSLR.

I guess color blind is from missing one of the cones. It's most common for people to have red-green color blind. I think it may be because M cone and L cone as so close to each other, and thus it's more likely for them to get confused.

For mobile graphics, it often uses tile based deferred rendering, which only one tile of primitives is rendered at one pass. The main reason is to reduce the memory traffic by increasing the spatial locality, as in mobile memory bandwidth is a big issue since GPU doesn't have dedicated DRAM as in desktop.

@acz I wonder if VR companies will start making headsets with prescription lens for a premium (or perhaps adjustable lenses you can tune in/out of focus slightly which may accomplish the same ends). Seems like a potential untapped marketing spin.

My understanding is that it differs based on the application, as games would likely require rays to be traced each frame, whereas a still photo wouldn't have such a requirement and thus could have rays "bounce" more times total to yield a more realistic image.

Exactly this. If I recall correctly, in class we simply used the two rays in the context of showing which rays intersected which primitives and bounding boxes first in each direction.

@amallery I believe so, but then I think that locality would be lost.

I personally find this example kind of scary ... lol

I'm also a bit confused on this, but I think that usually if we aren't able to exactly model a physical phenomena, then we end up making it a combination of smaller known convex pieces so that it can be efficiently computed.
Typically sprite animation is done with a set of pre-drawn images that represent different stages of motion and can be pieced together. This is an example of doing this in Unity: https://learn.unity.com/tutorial/introduction-to-sprite-animations