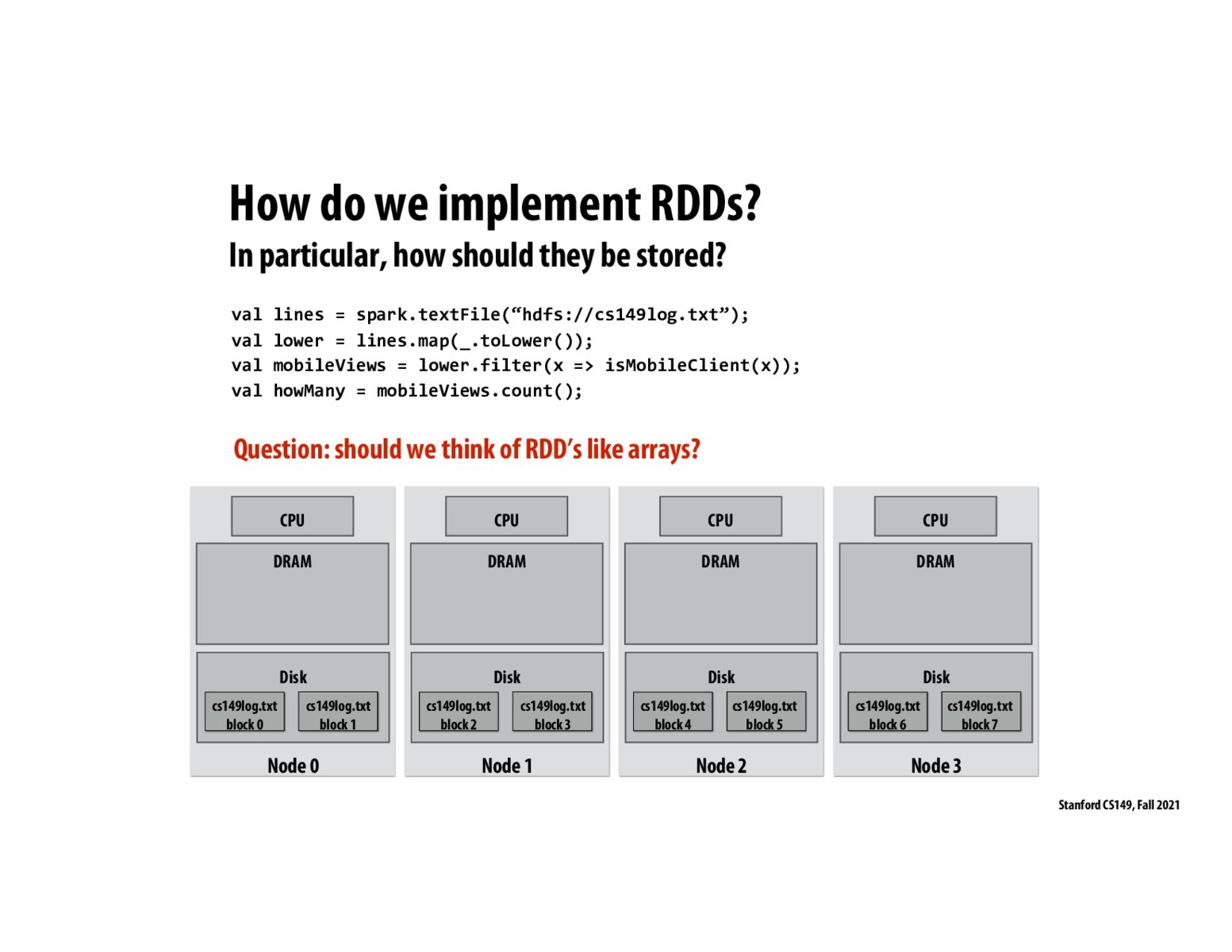


@nassosterz Referring back to Slide 31 and Spark's RDD Programming Guide, it seems to me that an RDD is simply a programming abstraction for Spark users. The Programming Guide also notes that "RDDs are created by starting with a file in the Hadoop file system (or any other Hadoop-supported file system), or an existing Scala collection in the driver program, and transforming it."
This guide gives additional details:
Internally, each RDD is characterized by five main properties:
- A list of splits (partitions)
- A function for computing each split
- A list of dependencies on other RDDs
- Optionally, a Partitioner for key-value RDDs (e.g. to say that the RDD is hash-partitioned)
- Optionally, a list of preferred locations to compute each split on (e.g. block locations for an HDFS file)
On this Stack Overflow post, the answer mentions that Spark creates DAGs of RDDs to keep track of operations.
In general, it seems that the programmer does not need to worry about how RDDs are represented in the HDFS files. It is more important to know the purpose and usage of the abstraction.
Please log in to leave a comment.
Can someone help me as to why specifically RDD's cannot be stored like arrays. Would space be the only limitation?
Or does the question relate to the abstraction of arrays and that RDD isnt applicable to be stored as a contiguous set of elements in memory.